India stands at a critical juncture in its energy transition. With a commitment to reach net-zero emissions by 2070 and to meet 50% of its energy needs from renewables by 2030, the nation is aggressively pursuing a diversified, sustainable energy mix. Yet, challenges remain, including dependence on imported fossil fuels, growing urban waste management crises, and the need for a just transition for its agriculture-dependent rural economy.
Enter Compressed Biogas (CBG) — a renewable fuel produced from organic waste sources like agricultural residue, municipal solid waste, and dairy waste. The Government of India’s SATAT scheme (Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation) aims to establish 5,000 CBG plants by 2030. But the true game-changer lies not just in producing CBG, but in seamlessly injecting it into the existing Piped Natural Gas (PNG) network.
This integration can decarbonize city gas distribution, provide clean cooking fuel, reduce landfill emissions, and create a circular economy — turning waste into worth. However, implementing this nationwide requires precision planning, real-time monitoring, and lifecycle management. This is where Geographic Information Systems (GIS) become indispensable, and Esri’s ArcGIS platform emerges as the foundational technology to orchestrate this energy revolution.
The CBG-PNG Integration Vision: A Systems Thinking Approach
Injecting CBG into PNG pipelines isn’t a simple plug-and-play. It requires a systemic view of:
1. Feedstock Logistics: Mapping and optimizing the collection of biomass from farms, landfills, and dairy clusters.
2. Plant Siting: Strategically locating CBG production plants near both feedstock sources and the PNG pipeline network.
3. Gas Grid Compatibility: Ensuring the calorific value and pressure of CBG meet pipeline specifications, requiring potential blending stations.
4. Demand-Supply Balancing: Dynamically matching CBG injection with urban and industrial gas demand patterns.
5. Monitoring & Safety: Continuously tracking gas quality, pipeline integrity, and injection points.
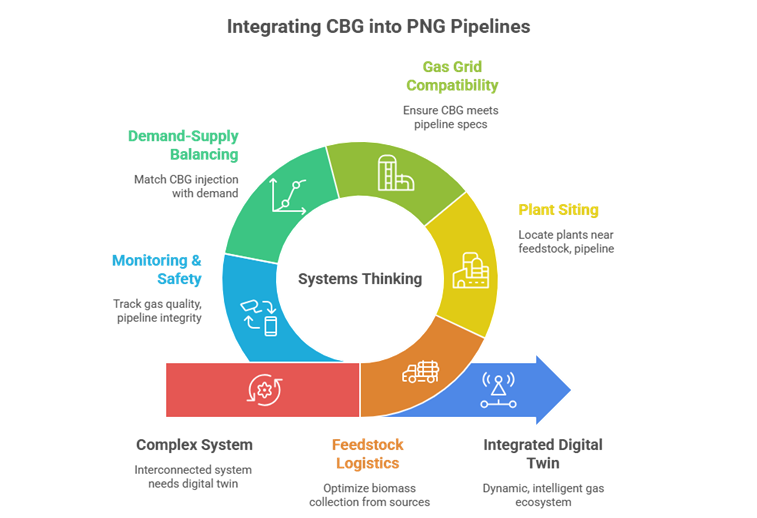
This complex, spatially interconnected system cannot be managed on spreadsheets or static maps. It needs a dynamic, intelligent, and integrated digital twin of India’s gas ecosystem.
The Esri ArcGIS Platform: Building the Digital Nerve Centre for India’s Green Gas Grid
Esri’s comprehensive GIS technology provides the framework to plan, implement, monitor, and optimize the entire CBG value chain. Here’s how:
1. Planning & Feasibility: The Where and How
Site Selection for CBG Plants: Using ArcGIS Pro with spatial analytics, planners can model the optimal location for CBG plants by analysing multi-layer data:
- Feedstock Availability: Proximity to paddy stubble fields (using satellite-derived crop residue maps), municipal waste processing sites, and sugarcane distilleries.
- Pipeline Proximity: Network analysis to find the shortest connection path to the existing PNG grid.
- Infrastructure & Constraints: Distance to roads, power lines, water sources, and avoiding ecologically sensitive or populated zones.
Pipeline Route Optimization: For new spur lines connecting plants to the main grid, ArcGIS Network Analyst can design the most cost-effective and least disruptive routes.
2. Operational Integration: The Digital Twin of the Gas Network
The Utility Network Model: This is the core. Esri’s ArcGIS Utility Network provides a modern, scalable data model to digitally represent India’s entire PNG infrastructure — pipelines, valves, compressors, meters, and now, CBG injection points.
Real-Time Monitoring Dashboard: Using ArcGIS Dashboards, gas distribution companies can gain a live, centralized view:
- CBG injection rates and volumes from each plant.
- Gas quality (Wobbe Index, methane content) at blending stations.
- Pressure and flow data along the pipeline network.
- Live Example: A dashboard for the Indore city gas network showing 20% of today’s gas mix is CBG from the local municipal waste plant, reducing carbon emissions by ‘X’ tons.
3. Logistics & Supply Chain Management
- Field Operations with ArcGIS Field Maps: Equip feedstock collection teams with mobile apps to log biomass collection, track truck routes, and report issues from remote fields.
- Fleet Tracking & Route Optimization: Use ArcGIS Location Tracking and Route Solver to manage the logistics of moving volatile organic waste to plants efficiently, reducing costs and emissions.
4. Regulatory Compliance & Public Engagement
- Transparent Reporting Portal: Use ArcGIS Experience Builder to create public-facing portals showing the impact of the CBG initiative. Citizens can see how much waste from their city is being converted to energy, and the resultant reduction in landfill and carbon emissions.
- Environmental Impact Tracking: Use ArcGIS Image Analyst with time-series satellite imagery to monitor the reduction in stubble burning in Punjab/Haryana as CBG plants absorb the residue.
5. Resilience & Risk Management
- Pipeline Integrity Management: Integrate GIS with IoT sensor data to visualize pipeline sections under stress or corrosion risk.
- Emergency Response: In case of an incident, ArcGIS Indoors and Evacuation Planning tools can help utilities manage safety protocols and communicate with emergency services.
The Bigger Picture: GIS as the Enabler of India’s Circular Economy
CBG injection is more than an energy project; it’s a blueprint for a circular economy. GIS connects the dots:
- Agriculture: Creates a new revenue stream for farmers from crop residue.
- Waste Management: Solves urban organic waste problems.
- Energy: Provides clean, affordable, and indigenous gas.
- Environment: Reduces methane emissions from landfills and CO2 from fossil fuels.
Esri’s platform acts as the integrating fabric, making this complex system visible, analysable, and manageable.
Partnering for a Sustainable India
The journey from waste to worth is inherently geospatial. To accelerate India’s net-zero journey through CBG integration, we propose a collaborative framework:
1. For Gas Utilities & CBG Producers: Adopt the ArcGIS Utility Network as the standard digital model for India’s integrated green gas grid. Start building your digital twin today.
2. For Government & Policymakers: Leverage ArcGIS Hub to create a National CBG-PNG Integration Geoportal for policy planning, incentive targeting, and transparent progress tracking against SATAT goals.
3. For Esri’s Ecosystem: Our network of experts, developers, and partners in India stands ready to support this national mission with solutions, training, and innovation.
The technology is here. The policy vision (SATAT) is in place. The need is urgent. By leveraging the power of location intelligence through the Esri platform, India can efficiently weave its organic waste into its energy fabric, creating a cleaner, more secure, and self-reliant future.

Swapnil is a seasoned GIS and Remote Sensing professional delivering enterprise GIS solutions for utilities, government, and infrastructure sectors.
